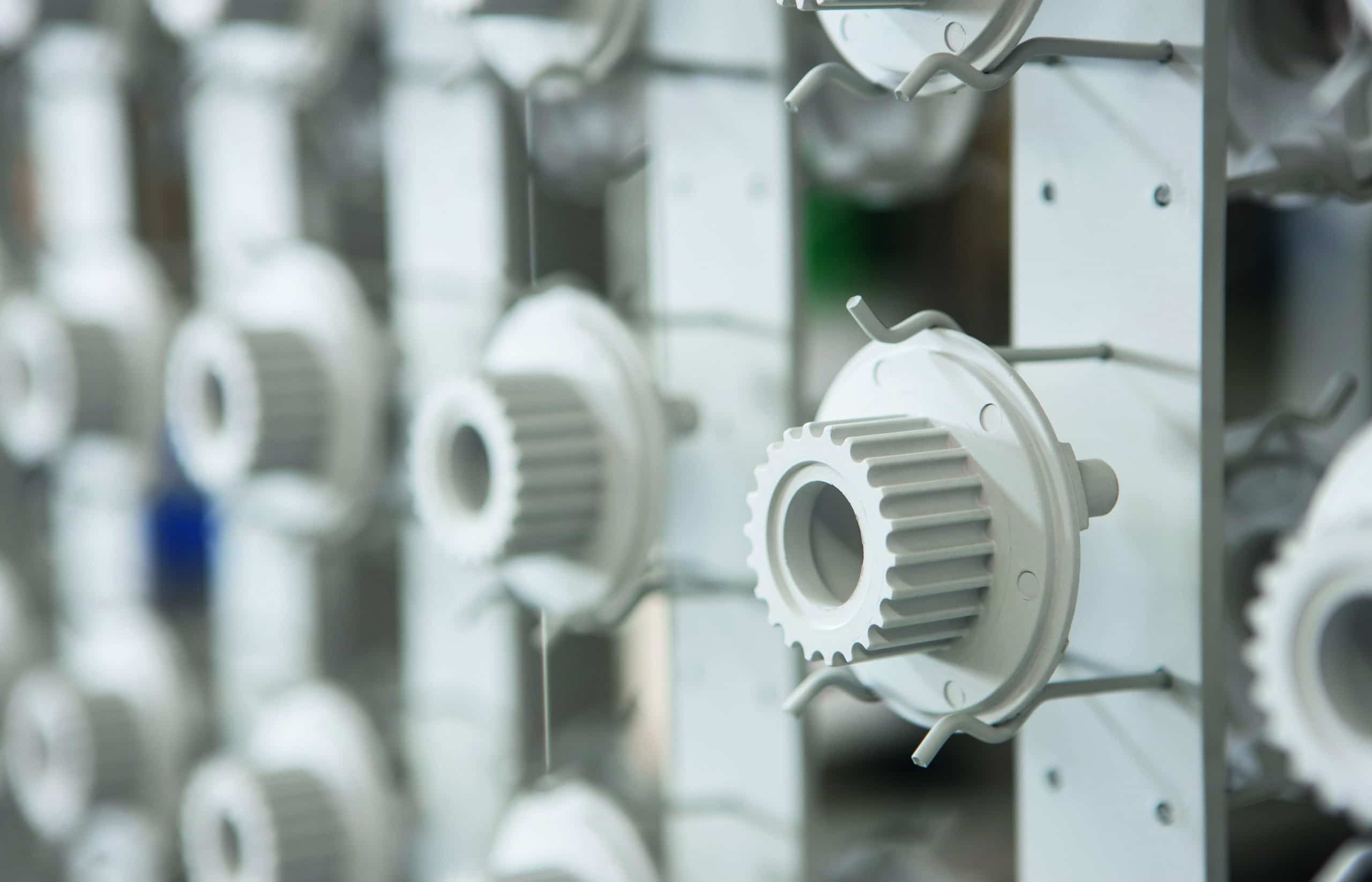
functional and decorative finishing of aluminum components as anode in special electrolytes
anodizing
what is anodizing?
Technical anodizing is a classic anodizing process performed in acidic electrolyte at a temperature slightly below ambient. An external power source is used, while the workpiece is used as anode. Anodized metal finishes provide many benefits, including a higher breaking strength, and an increased corrosion and wear protection. This electrochemical process is most frequently used to create anodized aluminum sheets and components, but we also provide anodized titanium finishes.
As a typical anodizing process, technical anodizing is carried out just below room temperature in an acid electrolyte. An external current source is used, with the workpiece to be coated connected as the anode.
The surface of the aluminum base material is transformed into aluminum oxide. One third of the coating created with technical anodizing grows out of the metal, whereas two thirds grow into it. That is why the bond between the coating and the base material is extraordinarily strong. What is more, coatings created with technical anodizing can meet different decorative requirements. To this end, preliminary treatments such as pickling, grinding, sandblasting or polishing are performed.
Aluminum-based alloys are becoming ever more popular as industrial construction materials. The low weight reduces inertia, which in turn saves energy. The disadvantage: aluminum alloys are prone to wear and corrosion.
Technical anodizing of metals such as aluminum or titanium is a functional coating solution delivering both protective and decorative results.
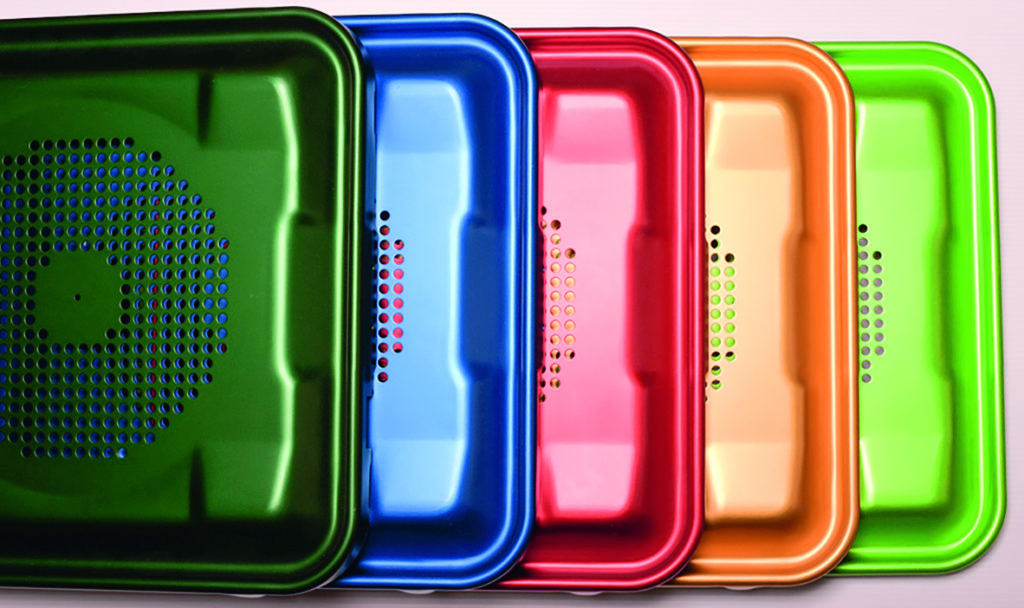
Anodization also makes dyeing possible: anodized aluminum and titanium can come in various colors, to achieve the functional or decorative effect desired. At Aalberts surface technologies, we offer, for example, both natural and black anodized aluminum finishes, but other colors are also possible using pigments.
anodized aluminum
Technical aluminum anodizing creates durable coatings in media which are neither too acidic nor too alkaline. Depending on the coating thickness and sealing, the coating is even able to temporarily withstand acidic or slightly alkaline attacks. The hardness of coatings created with technical anodizing is influenced by the material composition, especially by the alloy components. Coatings created with technical anodizing increase the wear resistance of aluminum to a significant extent.
anodizing of base materials
Be it wrought alloys, cast alloys or die-cast alloys, almost all technically interesting aluminum alloys can be finished with technical anodizing. However, the type of alloy has a major influence on the color of the product to be anodized. It is also possible to deliberately create black oxide coatings. In order for a base material to be recyclable, the finish too needs to fulfill the conditions for recyclability. Anodic coatings, such as those created with technical anodizing, meet this requirement – another advantage offered by this type of protective coating.
- Ideal protection against wear
- High corrosion protection
- Massive breaking strength
- Excellent tribological properties
- Protection against cold welding
- Electrical isolation
- Extreme temperature stability
Using different electrolytes and process parameters, we allow conductive oxide layers to “grow out” of the material such as metal. This anodizing process creates excellent structures and thus long-lasting surface finishes.
fields of use of anodic oxidation
Aluminum sheets and components finished with technical anodizing offer good corrosion and wear protection in almost all industries: construction industry, chemical industry, computer industry, electrical engineering, vehicle construction, household devices and goods, lighting industry, aerospace industry, mechanical engineering, medical technology, furniture and fittings industry, optics/precision engineering, sports and camping as well as the textile industry. Technical anodizing is also used to create a protective base layer which is applied prior to varnishing in order to protect components against corrosion.
Download technical anodizing
color anodized of aluminum and titanium materials
Thanks to the tried and tested surface finishes created by Aalberts surface treatment, it is easily possible to coat components with decorative colors and simultaneously protect them against corrosion. Components made of aluminum alloy are anodized in an electrolyte with color additives, whereas components made of titanium or titanium alloys are anodized in a special acidic electrolyte. The coating process creates a very thin, tenacious, colorless titanium oxide layer. It appears colored through interference (overlapping of light waves) and stands out with UV resistance. Using this method, we can create black, titan gray, blue, red, gold and green finishes. By varying the coating thickness, however, certain base materials may be finished in further colors. Apart from their color, titanium oxide coatings offer excellent electric isolation and biocompatibility.
the following base materials are suitable for color anodizing
Be it wrought alloys or cast alloys, almost all technically interesting aluminum alloys can be finished with color anodizing.
When it comes to titanium materials, however, things become a bit more complicated. The alloy most suitable for color anodizing is TiA16V4. The result: strong, reproducible colors of good quality.
Ti2 may also be coated in a wide range of colors. Unlike with TiAl6V4, the colors shift toward blue and appear somewhat subdued.
Reproducible color anodizing of pure titanium is limited to blue and yellowish finishes. This material is not suitable for decorative purposes.
scope of application of color anodizing
Color-anodized aluminum components can be used wherever decorative colors and protection against corrosion and wear are paramount. These requirements are found in the area of architecture as well as in the electrical engineering, image and video technology, household devices, hunting weapons, sports articles or bicycle industries. Of course, the process is also used to create coatings in the automotive industry or surface finishes in mechanical engineering.
Color-anodized titanium materials are also used in medical technology: Titanium-based implants, which remain inside the body for a limited period of time to promote the healing of bone fractures, for instance, are finished with color anodizing in order to allow surgeons to quickly identify the components concerned. The coated implants behave neutrally in the body. As they adhere neither to the bones nor to the tissue, they can be easily removed upon completion of the healing process.
Due to their biocompatibility and decorative look, colored titanium oxide coatings may also be used in the optics and jewelry industries, e.g. for watches or jewelry goods. The bicycle industry prefers titanium materials because they are light and yet extremely resilient. Using color anodizing processes, it is also possible to meet the design requirements of customers who are interested in purchasing wheel nuts, for instance.

industries we serve
frequently asked questions
So-called refractory metals – which include, amongst others, titanium, magnesium, zinc and vanadium – are suitable for anodizing. When it comes to the finishing of magnesium and titanium, Aalberts surface technologies offers two plasma-chemical processes: MAGOXID-COAT® (for magnesium) and KEPLA-COAT® (for titanium and aluminum).
Anodic coatings have an inherent color which depends on the aluminum alloy and the process parameters used, such as the electrolyte composition or temperature. Higher electrolyte temperatures result in brighter coatings, whereas greater coating thicknesses creates a darker layer, making it possible to create black anodized aluminum coatings. Anodic coatings have pores which form as a result of the anodizing process. It is possible to dye the coatings by introducing pigments into these pores.
White coatings are created using the KEPLA-COAT® white (for aluminum and titanium) and MAGOXID-COAT® white (for magnesium) processes. Here, too, the coating color depends on the alloy.
The maximum dimensions are 7700x1000x1800 mm³, whereas the weight is restricted to 5000 kg. However, these restrictions always depend on the coating plant.
These coatings are so-called conversion coatings. Parts of the base material become fully integrated with the coating, which results in an extremely high bonding strength between the anodic layers.
process locations
Any questions? Contact us directly or select a process location near you.
Helpfau-Uttendorf
Austria 48.168118113.1232299 uttendorf@aalberts-st.com +43 7724 44144 show locationBurg
Germany 52.2509811.88427 burg@aalberts-st.com +49 3921 4829 0 show locationDzierżoniów
Poland 50.732931316.6280222 dzierzoniow@aalberts-st.com +48 748108508 show locationGöppingen
Germany 48.66539429.6795345 eschenbach@aalberts-st.com +49 7161 15688 0 show locationHangzhou
China 30.274084120.15507 hangzhou@aalberts-st.cn +86 (571) 5757 9777 show locationKaufbeuren
Germany 47.91376710.6489502 kaufbeuren@aalberts-st.com +49 8341 6601 0 show locationKerpen
Germany 50.88076.6800999 kerpen@aalberts-st.com +49 2237 502 0 show locationKirchheim-Heimstetten
Germany 48.151143811.7440283 muenchen@aalberts-st.com +49 89 990241-0 show locationKirkby-In-Ashfield
United Kingdom 53.1043759-1.2474762 nottingham@aalberts-st.com +44 1623 753 107 show locationWeiterstadt
Germany 49.897638.61422 weiterstadt@aalberts-st.com +49 6151 9806 0 show locationBerlin
Germany 52.528455313.5331206 berlin@aalberts-st.com +49 30 549904 0 show locationVillers-Cotterets
France 49.24847423.1020097 info.villers@aalberts-st.com +33 323 9601 01 show locationUnsere Verfahren
Wir bieten weltweit alle Arten von Wärmebehandlungsprozessen an. Unsere Anlagen sind logistisch eng miteinander verknüpft, so dass Ihnen alle Verfahren zur Verfügung stehen. Erfahren Sie mehr zu unseren Wärmebehandlungsverfahren.
Heiß-Isostatisches Pressen (HIP) dient der Beseitigung von Porosität. Sie benötigen bei Lötverbindungen eine hohe mechanische Haltbarkeit und Unempfindlichkeit bei hohen Temperaturen? Wir bei Aalberts surface technologies bieten die Lösung durch Hartlöten (brazing).
Polymerbeschichtungen können auf viele Grundmaterialien aufgebracht werden und bieten lang anhaltenden Schutz. Sie sind mechanisch besonders gut mit dem Untergrund verankert und bieten verbesserte Gleiteigenschaften und/oder hohe Verschleißfestigkeit.
Mit 40 Jahren Erfahrung in der kontinuierlichen Veredelung von reel to reel können Sie sich auf Aalberts surface technologies verlassen, um innovative Lösungen zu finden. Unser Service umfasst Trommelgalvanik, kontinuierliche selektive Galvanik und Gestellgalvanik.
Fast alle metallischen Grundwerkstoffe können mit unseren selbstentwickelten und patentierten Verfahren durch Oberflächenbeschichtungen in ihren Eigenschaften optimiert werden, egal ob sie besonders hart, glatt, verschleißfest oder korrosionsbeständig sein sollen.

Discover our services
We offer all types of heat treatment processes. Our facilities are closely interlinked in terms of logistics, which means that all processes are available to you. For a complete list and description of heat treatment technologies please select the button.
Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is used to eliminate porosity. Do you need high mechanical durability and insensitivity to high temperatures for solder joints? We at Aalberts surface technologies offer the solution through brazing.
Polymer coatings can be applied to a wide variety of base materials and offer long-lasting protection. They are particularly well anchored mechanically to the substrate. Additional enhancement layers allow non-stick coatings to be combined with improved sliding properties and/or high wear resistance.
With 40 years of experience in continuous reel to reel finishing, you can depend on Aalberts surface technologies to find innovative solutions that other companies might say are impossible. Our service includes barrel plating, continuous selective plating and rack plating.
Almost all metallic base materials can have their properties optimised by surface coatings using our proprietary and patented processes, regardless of whether they should be particularly hard, smooth, wear-resistant or corrosion-resistant.

The Aalberts websites use cookies (read more) to analyse website usage and improve usability. We also use third party tracking-cookies to measure user preferences, enable content sharing on social media and interest-based advertising. If you hit 'accept' you allow to us to place the different types of cookies.
privacy overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 1 year | This cookies is set by GDPR Cookie Consent WordPress Plugin. The cookie is used to remember the user consent for the cookies under the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Others". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 1 year | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 1 year | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |